Introduction to 3D Printing and Its Evolution
3D printing, a form of additive manufacturing, has transformed the landscape of production since its inception in the early 1980s. Originally developed for rapid prototyping, this innovative technology has undergone substantial evolution, making significant strides in materials, techniques, and applications. The creative process begins with a digital model, which is sliced into layers by specialized software before being printed layer by layer, allowing for intricate and complex designs that traditional manufacturing methods often struggle to achieve.
The initial phases of 3D printing were characterized by the use of limited materials, primarily plastics and resin. However, advancements have broadened the range of usable materials to include metals, ceramics, and even bio-materials. This diversification has expanded the scope of 3D printing, enabling its application across various sectors, including aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and consumer goods. One notable evolution is the emergence of multi-material printing, which allows for the creation of objects with varied properties and functionalities within a single print, further enhancing its versatility.
Another critical component of the evolution of 3D printing is the development of software that streamlines the design and printing process. Enhanced modeling tools and simulation software have improved accessibility for users, enabling even those without extensive technical expertise to create complex designs. Additionally, cloud-based solutions have facilitated remote collaboration and sharing of resources, making 3D printing more integrated and responsive to industry needs.
As the technology has matured, its application has shifted from niche markets to mainstream adoption, positioning 3D printing as a disruptive force within the manufacturing sector. Businesses are increasingly recognizing its potential to reduce lead times, lower costs, and increase customization, thereby challenging conventional production paradigms and paving the way for a new era in manufacturing.
Key Applications Transforming Manufacturing Processes
3D printing technology, often referred to as additive manufacturing, is poised to revolutionize traditional manufacturing processes by enabling innovative applications across various industries. One of the most significant areas where 3D printing has made an impact is in prototyping. Rapid prototyping allows companies to produce physical models quickly, facilitating a faster design process that enhances product development. This capability is especially beneficial in sectors like automotive and aerospace, where design iterations can occur swiftly, resulting in shorter lead times and cost savings.
In addition to prototyping, 3D printing is being increasingly utilized for producing end-use parts, which marks a considerable shift in traditional supply chains. Industries such as aerospace, which requires lightweight and customized components, benefit immensely from additive manufacturing’s ability to create complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional methods. Furthermore, reducing material waste is a crucial advantage; with 3D printing, only the necessary material is used, contributing to more sustainable practices within manufacturing.
The healthcare sector is another area seeing transformative applications of 3D printing. Custom implants and prosthetics tailored to individual patients can be produced, significantly improving patient outcomes and reducing operation times. For instance, several medical institutions have successfully implemented 3D printing technologies to manufacture surgical guides and anatomical models, providing surgeons with accurate representations of their patients’ unique anatomical features.
Moreover, the consumer products industry is leveraging 3D printing to customize items for users, allowing for personalized designs and functionalities. Companies are increasingly adopting 3D printing to create small batches of customized goods, which reduce the constraints of mass production. Overall, these applications illustrate how 3D printing is not only enhancing efficiency and reducing time to market but also paving the way for innovative solutions across multiple sectors.
Challenges and Considerations for Adoption
As manufacturing companies consider integrating 3D printing technologies into their operations, various challenges and considerations come to the forefront. One significant factor to address is the cost of adopting 3D printing solutions. While the initial investment may be substantial, businesses must evaluate the potential for long-term savings and efficiency improvements. The procurement of advanced printers, materials, and supporting software represents a considerable capital commitment, especially for smaller enterprises. Manufacturers must conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses to ascertain whether the financial outlay aligns with their operational objectives.
Another critical aspect is the scalability of 3D printing technologies. Companies must ascertain whether the current capacities of 3D printers can meet their production volume requirements. While additive manufacturing excels in producing complex geometries and customized items, transitioning from prototyping to mass production can pose challenges. Manufacturers need to identify appropriate 3D printing techniques and technologies that cater to scalability while maintaining speed and reliability in the production process.
Quality control is also vital when adopting 3D printing in manufacturing. Ensuring consistent quality across batches can be complicated due to variations in the printing process, materials, and even machine settings. A robust quality assurance framework must be established to monitor and address these potential fluctuations, which may involve redefining standards for product acceptance. Furthermore, manufacturers must navigate regulatory hurdles, ensuring that their 3D-printed products comply with industry standards and safety regulations, which often require intricate documentation and testing protocols.
Lastly, the successful integration of 3D printing into existing production workflows necessitates workforce retraining. Traditional manufacturing roles may require new skills related to 3D modeling, machine operation, and maintenance. Companies must invest in training programs to equip employees with the requisite knowledge and skills to adapt to this evolving landscape of manufacturing. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for businesses looking to fully harness the potential of 3D printing and solidify their competitive advantage in the market.
The Future of 3D Printing in Manufacturing
As we look ahead to the future of 3D printing in the manufacturing sector, it is evident that this technology is poised to significantly transform how products are designed, produced, and distributed. Innovations such as bioprinting and multi-material printing are likely to become increasingly prevalent. Bioprinting, which involves creating biological tissues and organs, holds promise for the medical field, enabling personalized healthcare solutions. Meanwhile, multi-material printing will facilitate the creation of complex structures with diverse material properties, broadening the scope of what can be manufactured.
Automation in 3D printing processes is another area of anticipated growth. With advancements in robotics and artificial intelligence, we can expect a streamlined approach to production cycles. Automation will enhance precision, reduce human error, and ultimately lead to cost savings. By integrating automated systems, manufacturers can keep up with the demand for rapid prototyping and short-run production, allowing for faster time-to-market and greater innovation.
Furthermore, one of the most significant advantages of 3D printing is its potential to enable mass customization. This capability will allow manufacturers to tailor products to the specific needs and preferences of consumers, creating unique items at scale. The shift towards personalized manufacturing can disrupt traditional supply chains, reducing the need for large inventories and minimizing waste.
As the landscape of 3D printing evolves, emerging market trends will shape future collaborations and competition within the industry. Companies will increasingly partner to enhance technological capabilities and share resources. The integration of new materials, improved software, and sustainable practices will further define the competitive edge in the manufacturing realm. Thus, the future of 3D printing holds vast potential, ushering in an era marked by innovation and efficiency.

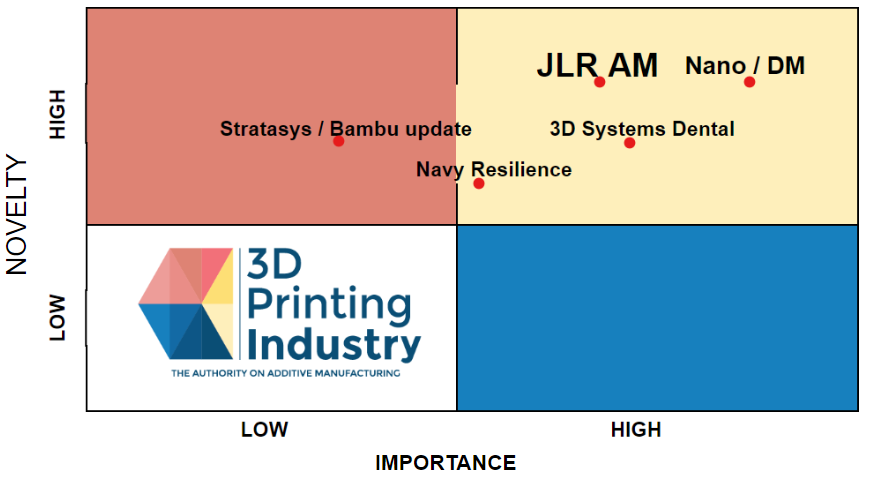
Leave a Reply